Testing
Unit Tests
Unit testing is an important part to ensure that changes on our codebase does not break existing features and functionalities. For Zap, we mainly use pytest, a Python testing framework.
Creating Test File
All unit tests are created under the tests directory, and each directory and/or file would correspond to each file in chalicelib and the application itself. For example, if we wanted to create unit tests for chalicelib/services/ApplicationService.py, we would create a file like tests/services/test_application_service.py.
Creating and Running Tests
NOTE: All test files names must have the prefix test_
To create a test, create a function with the prefix name test_, and proceed with unit testing.
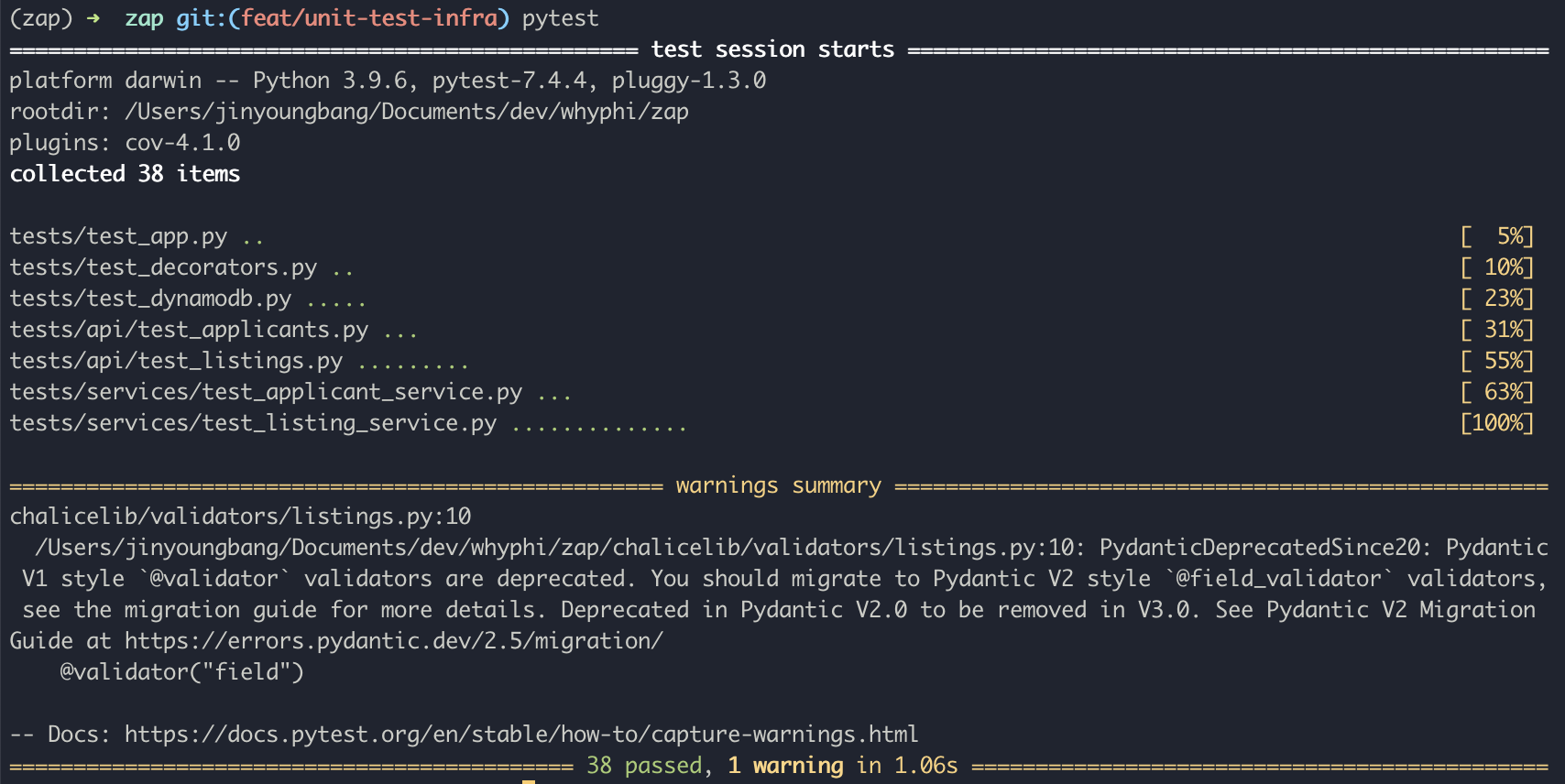
To run the unit test, run the pytest command and it will show if you passed or failed any tests.
Code Coverage
Code coverage is a metric that can help you understand how much of your source is tested. It’s a very useful metric that can help you assess the quality of your test suite.
To run and generate the code coverage report, run make coverage. You will have re-run this command everytime you make changes to your unit test suite.
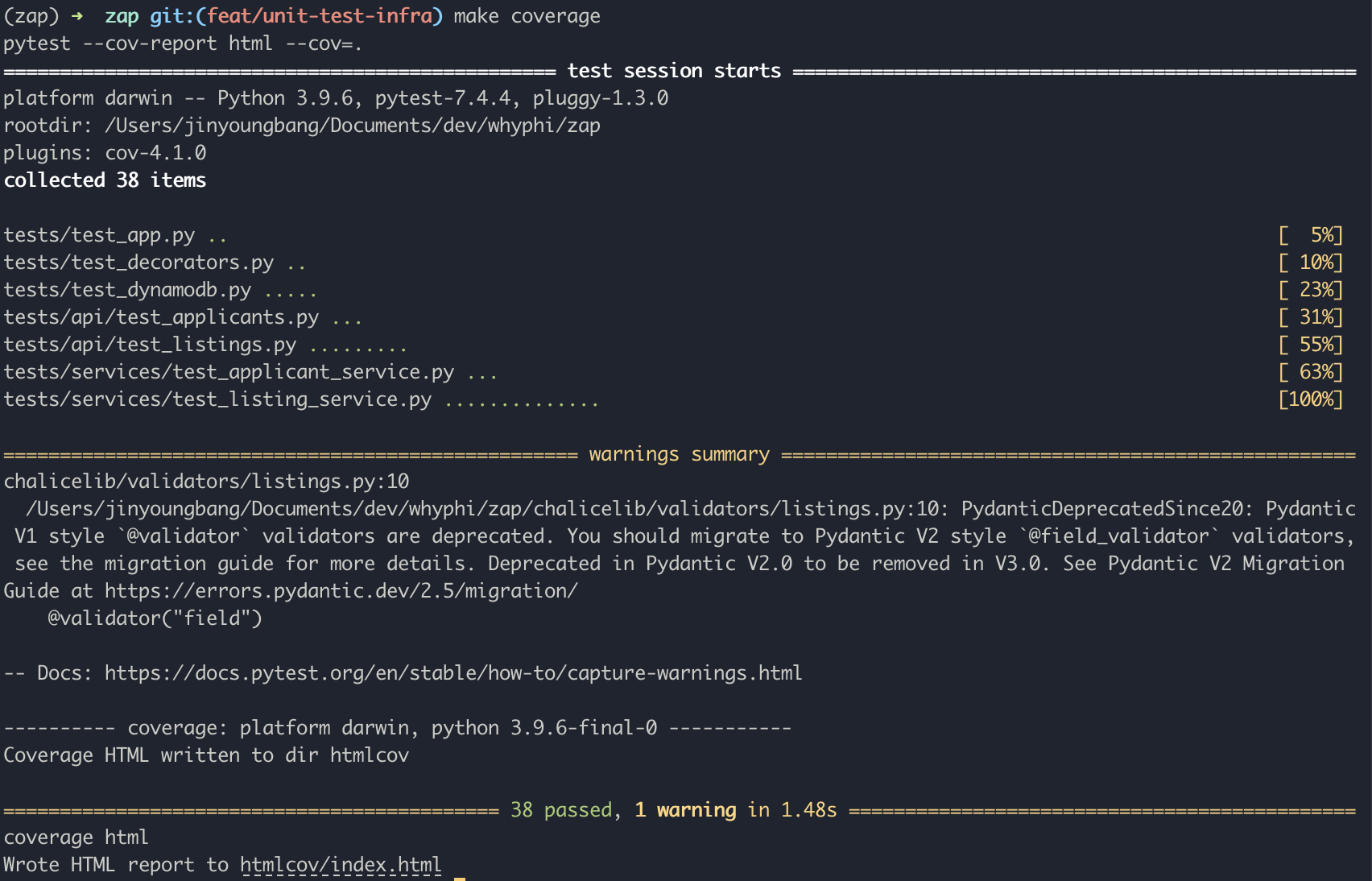
To view the code coverage report, open htmlcov/index.html and it will give a summary of how much code was covered from the unit tests. Click on a specific file from the report to get a detailed view of which lines were covered and not.
The green lines indicate that the unit tests hit these lines, where as the red lines mean the opposite. For this example, we can see that the else case and the exception case on delete_item was not tested in the db.py file: